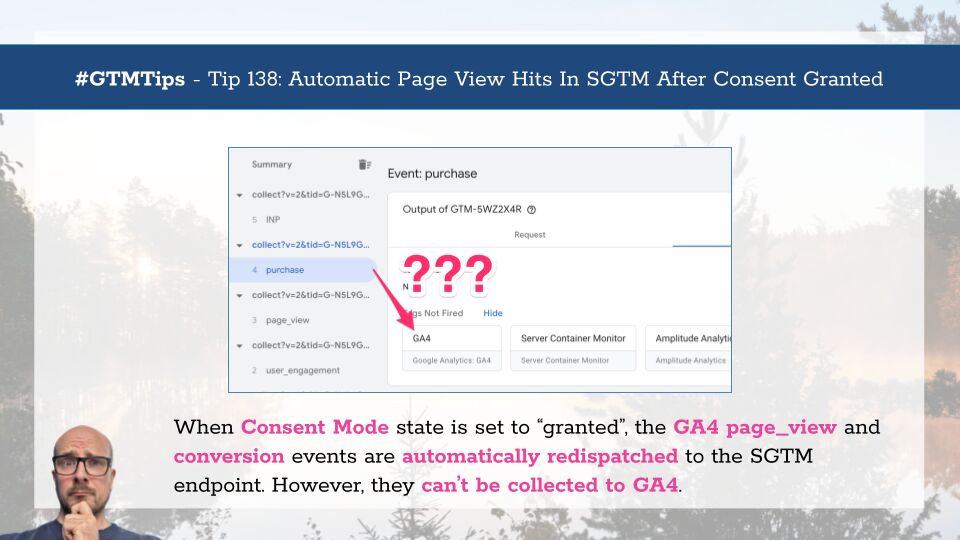
If you’re using server-side Google Tag Manager, Google (Advanced) Consent Mode and you’re collecting hits to Google Analytics 4, you might have noticed something odd happening when switching consent to granted state.
It looks as if your page_view hits as well as any other hits marked as “Conversions” (or key events now, I guess) are automatically redispatched to the server-side Google Tag Manager endpoint when consent is granted!
This sounds incredibly useful.